“Helm + ArgoCD + ApplicationSet으로 구축하는 PR Preview 환경 (1편: 아키텍처)”
앞선 글과 이어지는 내용 입니다.
2편 글에서는 Preview 환경을 Helm 차트로 어떻게 만들었는지 설명해보도록 하겠습니다.
Helm 차트를 왜 선택했는가?
PR 마다 네임스페이스가 달라지고, 각 어플리케이션 파드 별로 이미지가 달라지는 상황에서 k8s yaml을 일일히 변경하면 비효율적이고, 실수를 하게될 위험이 큽니다.
Helm은 템플릿화가 가능해서, PR 번호나 이미지 태그 같은 값을 변수로 넘길 수 있어 변화가 잦은 Preview 환경에 적합하다 생각되어 선택하였습니다.
이제 Helm 차트를 어떻게 생성하고 구성했는지 알아보겠습니다.
Helm 차트 생성
- Helm 차트 생성 명령어
helm create myproject위 명령어로 Helm 차트를 생성하면 디렉터리 tree 구조가 아래와 같이 생성이 됩니다.
myproject
├── Chart.yaml # Chart의 메타데이터 정의하는 파일 (이름, 버전, 설명 등)
├── charts # 서브차트 저장 위치 (다른 Chart를 종속성으로 포함할 때 사용, 이번엔 사용 x)
├── templates # k8s 리소스 매니페스트가 정의되는 핵심 디렉터리
│ ├── NOTES.txt
│ ├── _helpers.tpl
│ ├── deployment.yaml
│ ├── hpa.yaml
│ ├── ingress.yaml
│ ├── service.yaml
│ ├── serviceaccount.yaml
└── values.yaml # Helm 차트의 변수들을 모아놓은 환경설정 파일, values.yaml 파일에 정의된 값을 보고 templates/*.yaml 파일에서 참조하여 리소스를 동적을 생성합니다.처음에 해당 Helm 차트의 Tree 구조를 보면 이해가 안될 수 있습니다.
이제 제가 작성한 Yaml 파일을 보면서 좀 더 자세히 알아보겠습니다.
저는 먼저 values.yaml 파일에 변수 구성을 먼저 정의 하였습니다.
values.yaml 파일 구성
# === 전역 공통 옵션 ===
global:
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# 모든 파드에 공통 라벨/Taint 정의
commonLabels: {}
tolerations:
- key: "spot"
operator: "Equal"
value: "only"
effect: "NoSchedule"
affinity: {}
# 모든 파드에 공통 ENV / ENVFROM (필요 없으면 빈 배열)
env: []
envFrom: []
# 예시:
# env:
# - name: LOG_LEVEL
# value: info
# envFrom:
# - secretRef: { name: shared-app-secret, optional: true }
# === ALB(shared)용 Ingress 룰 추가 ===
ingress:
enabled: true
# (기존 ALB 재사용하기 위한 shared ALB 그룹 이름). 템플릿에서 group.name에만 사용
groupName: "shared-alb"
className: "alb" # ALB IngressClass 이름
# === ESO 설정 ===
externalSecret:
store:
kind: ClusterSecretStore
name: dev-outcode-cluster-secretstore
refreshInterval: 1m
# === 애플리케이션 목록 ===
components:
# ------ Front ------
front:
enabled: true
image: "<이미지 이름>"
tag: "<이미지 태그 이름>"
replicas: 1 # 원하는 레플리카 개수 정의
containerPort: 80 # 실제 파드에서 사용하는 컨테이너 포트 정의
nodeSelector: # 파드가 생성될 노드 지정
node-type: spot
service:
enabled: true
port: 80
ingress:
enabled: true
host: <ingress 에서 사용할 원하는 호스트 명>
paths:
- path: /
serviceName: front
servicePort: 80
# ExternalSecret 리소스에서 사용할 변수 정의
secret:
smKey: <AWS SecretManager에서 사용하는 SM 이름> # Base: SM에서 읽기
k8sName: <k8s에서 사용할 Secret 리소스의 이름>
overrides: # Preview 환경에서만 사용할 Secret Key/Value (SM은 안 건드림)
test: test
envFrom:
- secretRef: { name: <k8s에서 사용할 Secret 리소스의 이름>, optional: true }
resources:
requests: { cpu: 100m, memory: 256Mi }
limits: { cpu: 200m, memory: 512Mi }values.yaml 파일에 작성한 변수들에 대해 설명을 하자면,
- Preview 환경을 Spot 인스턴스에 띄우기 위해
tolerations과nodeSelector지정 - ingress 전역 설정에는
ingress 애노테이션에 정의될 사항들,component.front에서 정의한 ingress 변수는path 경로를 지정했습니다. - 그리고 AWS SecretManager에 등록 시켜둔 환경 변수를 참조하기 위해 ESO 변수를 지정을 해두었습니다.
component.front.secret.overrides이 부분이 중요한 게, SecretManger에 저장된 값을 그대로 사용하는 것이 아닌, Preview 환경에서만 사용할 변수로 덮어 쓰기 위해서 정의를 해두었습니다.- 현재는
component에front밖에 없지만, 제가 사용한 실제values.yaml파일에는 여러 개의 애플리케이션들을 정의 해두었습니다. - 형식은 동일하고 변수 값만 다르게 설정을 하였습니다.
이제 values.yaml 파일의 변수 값들을 참조하여 templates/*.yaml 파일들의 내용을 구성 해보겠습니다.
templates/*.yaml 파일 구성
저 같은 경우에는 templates에서 사용할 파일들이 아래와 같습니다.
- deployment.yaml
- externalsecret.yaml
- ingress.yaml
- namespace.yaml
- service.yaml
deployment.yaml
{{- /*
모노차트용 공통 Deployment 생성기
- components.<name>.* 스키마에 맞춤
*/ -}}
{{- range $name, $c := .Values.components }}
{{- if $c.enabled }}
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ $name }}
namespace: {{ $.Release.Namespace }}
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ $name }}
spec:
replicas: {{ $c.replicas | default 1 }}
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ $name }}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ $name }}
{{- with $.Values.global.commonLabels }}
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
spec:
{{- /* nodeSelector: global + component(있으면 덮어쓰기) */}}
{{- $nodeSel := merge (deepCopy ($.Values.global.nodeSelector | default dict)) ($c.nodeSelector | default dict) }}
{{- if $nodeSel }}
nodeSelector:
{{- toYaml $nodeSel | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
{{- /* tolerations: global + component */}}
{{- $tols := concat ($.Values.global.tolerations | default list) ($c.tolerations | default list) }}
{{- if $tols }}
tolerations:
{{- toYaml $tols | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
{{- with $.Values.global.affinity }}
affinity:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
containers:
- name: {{ $name }}
image: "{{ $c.image }}:{{ $c.tag }}"
imagePullPolicy: {{ $.Values.global.imagePullPolicy | default "IfNotPresent" }}
ports:
- containerPort: {{ $c.containerPort }}
{{- /* env: global + component */}}
{{- if or $.Values.global.env $c.env }}
env:
{{- with $.Values.global.env }}{{ toYaml . | nindent 12 }}{{- end }}
{{- with $c.env }}{{ toYaml . | nindent 12 }}{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- if or $.Values.global.envFrom $c.envFrom }}
envFrom:
{{- with $.Values.global.envFrom }}{{ toYaml . | nindent 12 }}{{- end }}
{{- with $c.envFrom }}{{ toYaml . | nindent 12 }}{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- with $c.resources }}
resources:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 12 }}
{{- end }}
---
{{- end }}
{{- end }}- 이
deployment.yaml은components를 순회(range)하면서 컴포넌트 별 deployment를 생성합니다. - {{- range $name, $c := .Values.components }} 설명을 하자면,
values.yaml파일에서 정의한components키를 참조합니다. - 예를 들어 앞서 작성한
values.yaml파일을 생각해보면,$name은components.front같은components하위의 애플리케이션 이름 입니다. $c=components.front라고 생각을 하시면 되고, 위에서 보면$c.image는components.front.image의 값이라고 생각을 하시면 됩니다.
이제 다른 templates/*.yaml 파일들의 내용을 보여드릴텐데, deployment.yaml 과 비슷하게 , values.yaml 파일에서 정의해둔 변수들을 사용한다고 생각하시면 됩니다.
service.yaml
{{- /*
모노차트용 공통 Service 생성기
- 각 컴포넌트에서 service.enabled=true 일 때 생성
*/ -}}
{{- range $name, $c := .Values.components }}
{{- if and $c.enabled $c.service.enabled }}
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: {{ $name }}
namespace: {{ $.Release.Namespace }}
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ $name }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ $.Release.Name }}
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ $name }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ $.Release.Name }}
ports:
- name: http
port: {{ $c.service.port }}
targetPort: {{ $c.containerPort }}
---
{{- end }}
{{- end }}namespace.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Namespace }}
annotations:
# NS가 제일 먼저 생성되도록
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "-1"네임스페이스 같은 경우 원래는 template에 없었는데, ArgoCD 를 사용해서 배포를 할 때,
관리하는 리소스에 없으면 네임스페이스를 생성만 하고 지우질 않아서 template 리소스에 추가를 했습니다.
externalsecret.yaml
{{- range $name, $c := .Values.components }}
{{- if and $c.enabled $c.secret $c.secret.smKey $c.secret.k8sName }}
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: {{ $c.secret.k8sName }}
namespace: {{ $.Release.Namespace }}
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: {{ $name }}
spec:
refreshInterval: {{ $.Values.externalSecret.refreshInterval | default "30m" | quote }}
secretStoreRef:
name: {{ $.Values.externalSecret.store.name | quote }}
kind: {{ $.Values.externalSecret.store.kind | default "ClusterSecretStore" | quote }}
target:
name: {{ $c.secret.k8sName }}
creationPolicy: Owner
{{- if $c.secret.overrides }}
template: # PR 전용 덮어쓰기 (SM은 안 건드림)
mergePolicy: Merge
engineVersion: v2
type: Opaque
data:
{{- range $k, $v := $c.secret.overrides }}
{{ $k }}: {{ $v | quote }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
dataFrom:
- extract:
key: {{ $c.secret.smKey | quote }} # Base: SM에서 읽기
---
{{- end }}
{{- end }}ingress.yaml
{{- range $name, $c := .Values.components }} # values.components를 돌면서 각 컴포넌트(예: front, api)를 처리
{{- if and $c.enabled $c.ingress $c.ingress.enabled }} # 컴포넌트가 활성화되어 있고, ingress도 활성화된 경우에만 Ingress 생성
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-{{ $name }}
namespace: {{ $.Release.Namespace }}
annotations:
# IngressClass 지정(주요 컨트롤러 선택). AWS ALB의 경우 className "alb" 사용
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: {{ default "alb" $root.Values.ingress.className | quote }}
# 같은 ALB를 공유하려면 group.name을 동일하게 지정 (shared ALB 패턴)
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/group.name: {{ $root.Values.ingress.groupName | quote }}
# ExternalDNS TTL 설정 (Route53 레코드 TTL)
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl: "60"
# AWS ALB 관련 표준 어노테이션들
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing # 인터넷 공개형 ALB
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip # 타깃 타입: Pod IP
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80}, {"HTTPS": 443}]' # 리스너 포트
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: arn:aws:acm:ap-northeast-1:308910977993:certificate/ca51fb3a-3b14-4e21-825e-48278b51c6d7
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: '443' # HTTP → HTTPS 리다이렉트
{{- with $c.ingress.annotations }} # 컴포넌트 개별 Ingress에 추가로 넣을 어노테이션 병합
{{- toYaml . | nindent 4 }}
{{- end }}
spec:
# spec에도 IngressClassName 설정 (annotation 방식보다 권장)
ingressClassName: {{ default "alb" $root.Values.ingress.className | quote }}
rules:
- host: {{ $c.ingress.host | quote }} # 이 컴포넌트에 매핑할 호스트 (예: pr-front.outcode.ai)
http:
paths:
{{- range $p := $c.ingress.paths }} # 이 컴포넌트에 대한 path 라우팅 목록 순회
- path: {{ $p.path }} # 라우팅 경로 (예: "/")
pathType: {{ default "Prefix" $p.pathType }} # PathType (기본 Prefix)
backend:
service:
# 백엔드로 붙일 Service 이름: <릴리스fullname>-<컴포넌트명>
# Service 템플릿에서도 같은 네이밍 규칙을 써야 정확히 매칭됨!
name: {{ default $name $p.serviceName }}
port:
# 우선순위: path에 지정한 servicePort → 컴포넌트의 service.port
number: {{ $p.servicePort | default $c.service.port }}
{{- end }}
---
{{- end }}
{{- end }}이제 Helm 차트를 Packing 해서 Push 하기 전, 이름과 버전을 지정해줍니다.
Chart.yaml
apiVersion: v2
name: <원하는 Helm 차트 이름>
description: A Helm chart for Kubernetes
# A chart can be either an 'application' or a 'library' chart.
#
# Application charts are a collection of templates that can be packaged into versioned archives
# to be deployed.
#
# Library charts provide useful utilities or functions for the chart developer. They're included as
# a dependency of application charts to inject those utilities and functions into the rendering
# pipeline. Library charts do not define any templates and therefore cannot be deployed.
type: application
# This is the chart version. This version number should be incremented each time you make changes
# to the chart and its templates, including the app version.
# Versions are expected to follow Semantic Versioning (https://semver.org/)
version: <Repository에 올려둘 버전 지정>
# This is the version number of the application being deployed. This version number should be
# incremented each time you make changes to the application. Versions are not expected to
# follow Semantic Versioning. They should reflect the version the application is using.
# It is recommended to use it with quotes.
appVersion: "1.16.0"여기서 중요한 점은, Helm 차트의 템플릿 내용이 변경되거나 아니면 values.yaml 파일의 구조가 변경되면 Chart.yaml 파일의 version을 계속해서 변경해줘야 합니다.
이유는 아래와 같습니다.
- 차트 패키징/푸시할 때 구분자 역할을 위해
- 같은 버전으로 패키징/푸시 하면 ArgoCD에서 Helm Release 캐싱 때문에 업데이트가 안될 수 있습니다.
이제 Helm 차트 패키징하고 ECR에 푸시 해보도록 하겠습니다.
Helm 차트 패키징/푸시
- Helm 패키징 명령어
helm package ./myproject위 명령어를 사용해서 패키징하면, *-<version>.tgz 파일이 하나 생성됩니다.
그리고 저 같은 경우 Repository를 ECR로 사용을 해서 ECR 로그인을 하였습니다.
- Helm 차트 푸시 전 ECR 로그인
aws ecr get-login-password \
--region <리전 명> | helm registry login \
--username AWS \
--password-stdin <ECR 레포지터리 이름>공식문서에 나온 명령어를 참조하였습니다.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/ko_kr/AmazonECR/latest/userguide/push-oci-artifact.html
이제 푸시 해보도록 하겠습니다.
- Helm 차트 푸시 명령어
helm push *-<version>.tgz oci://ECR 주소/그러면 아래 이미지 처럼 ECR에 Helm Chart 가 생기게 됩니다.
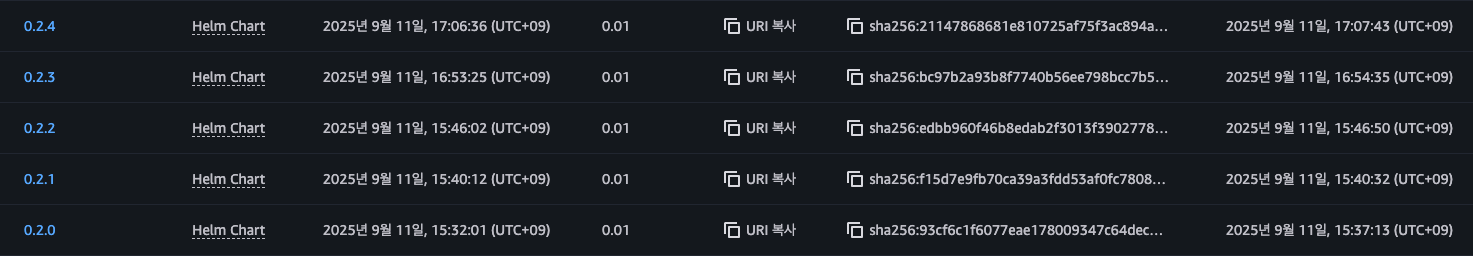
다음 글에서는 생성한 Helm Chart를 가지고 개발자가 PR을 생성했을 때,
어떻게 배포가 되는지 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
감사합니다.
'Pipeline' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Github Action에서 Docker Build 시간 줄이기 (1) | 2025.11.12 |
|---|---|
| “Helm + ArgoCD + ApplicationSet으로 구축하는 PR Preview 환경 (3편: Preview 환경 배포하기)” (0) | 2025.09.16 |
| “Helm + ArgoCD + ApplicationSet으로 구축하는 PR Preview 환경 (1편: 아키텍처)” (0) | 2025.09.11 |
| ArgoCD 배포 완료 시, Google-Chat으로 알림 보내기 (Helm 차트의 values.yaml 파일 수정) (0) | 2025.06.23 |
| Blue - Green 배포 실습 해보기 (1) | 2024.12.20 |